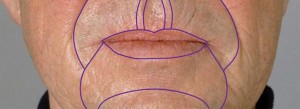
“The introduction of the concept of the regional aesthetic units in facial reconstruction improved the aesthetic outcome and thus the quality of life of affected patients”
Development and perspectives in reconstructive plastic surgery of the face
The foundation of the reconstructive plastic surgery of the face goes back to the beginning of the 19th century. The aim was to reconstruct facial defects after war wounds, infections, congenital defects and skin cancer. Over the years, the causes of facial defects did not change; moreover the skin cancer is increasing, mostly because of sun exposure.
The surgical strategy in facial reconstruction was profoundly influenced by the introduction of the concept of the regional aesthetic units of the face in the 50th for the treatment of burn victims, improving the aesthetic outcome and thus the quality of life of affected patients; flap design became simpler. Furthermore, the introduction of diagnostic ultrasound (Doppler) made possible the design of arterial flaps with more accuracy.
Malignant skin tumors, diagnosis and treatment
The dermatoscope, a magnifying optical instrument, has become a standard tool for the diagnosis of pigmented skin lesions and skin tumors. Skin digitized images make the early diagnosis easier and thus improve the follow-up. Cooperation with a dermatologist for body check-up is mandatory in presence of skin cancer of the face. A supplemental ultrasound examination of the lymphatic nodes in the head and neck region is mandatory. Depending on the findings, further radiological examinations are carried out. In addition to the diagnosis and planning of the operation, the surgical procedure, according to the anatomical location in the head and neck, is of great importance as mentioned under “Treatment”.
Benign skin lesion
Birthmarks (Nevus/Nevi) and other benign skin lesions are not only aesthetically disturbing, they can (in rare cases) transform into a malignant lesion. The therapy is simple for small lesions; nevertheless big lesions are very challenging and more complex flaps are necessary. In some selected cases, laser treatment is an alternative.
Surgery of the paralyzed face
Long lasting facial paralysis should be treated by facial suspension involving the lip muscle. The eyelid closure can be corrected by using eyelid implants. Botulinum toxin therapy in the unaffected side in combination with a classical surgical correction of the affected side, leads to an improvement of face symmetry.
Surgery of the orbit | Eye socket:
We perform corrective surgery to the eye socket (bone) but also on the lids. Corrective eye socket (orbit) surgery is often necessary after trauma (fracture) or tumor (as fibrous dysplasia). Thyroid orbitopathy (eyeballs that stick out in patients suffering hyperthyroidism / Graves’ disease) are operated in close cooperation with the internist and ophthalmologist. The aim of the surgery is to reduce the increased fat from the eye socket via a blepharoplasty access (surgical approach in aesthetic lid surgery) and thus normalizing the appearance of the eyes; more details are available under “Treatment”, “Orbit/ Eye socket”.
 Treatment
Treatment
Localization & Treatment (Common description vs. Medical description)
-
Scalp
· Treatment: Closure by using local tissue, skin expansion; Medical description: Local flaps, Tissue expansion.
-
Forehead
· Treatment: Closure by using local tissue, skin expansion; Medical description: Local flaps, Tissue expansion.
-
Eyebrow
· Treatment: Closure by using local and distant tissue; Medical description: Full-thickness defect: Temporal artery flap.
-
Lids
· Treatment: Closure by using local and distant tissue; Medical description: Transposition flaps, pedicle flap of opposite eyelid, connective tissue graft, rotational cheek flap, glabella VY flap.
-
Nose
· Treatment: Closure by using local and distant tissue; Medical description: VY glabella flap, fronto-axial-flap, forehead flap (median and paramedian flap).
-
Ears
· Treatment: Closure by using local and distant tissue; Medical description: Local flaps.
-
Cheek
· Treatment: Skin expansion; Medical description: Cheek rotation flap, tissue expander, local transposition flaps.
-
Lips
· Treatment: Closure by using local tissue; Medical description: Step stair technique (Johanson), Abbé flap, double Abbé flap, nasolabial flap, vermilionectomy and reconstruction acc. to von Bruns.
-
Chin
· Treatment: Closure using local tissue; Medical description: Local transposition flaps (Szymanowski flap).
-
Neck
· Treatment: Closure by using local tissue; Medical description: Local flaps, bilobed flap.